


The National Science Foundation (NSF) is an independent federal agency created by Congress in 1950 "to promote the progress of science to advance the national health, prosperity, and welfare to secure the national defense."ĪUI collaborates with the scientific community and research sponsors to plan, build, and operate cutting-edge facilities. NRAO also provides both formal and informal programs in education and public outreach for teachers, students, the general public, and the media. Observing time on NRAO telescopes is available on a competitive basis to qualified scientists after evaluation of research proposals on the basis of scientific merit, the capability of the instruments to do the work, and the availability of the telescope during the requested time.
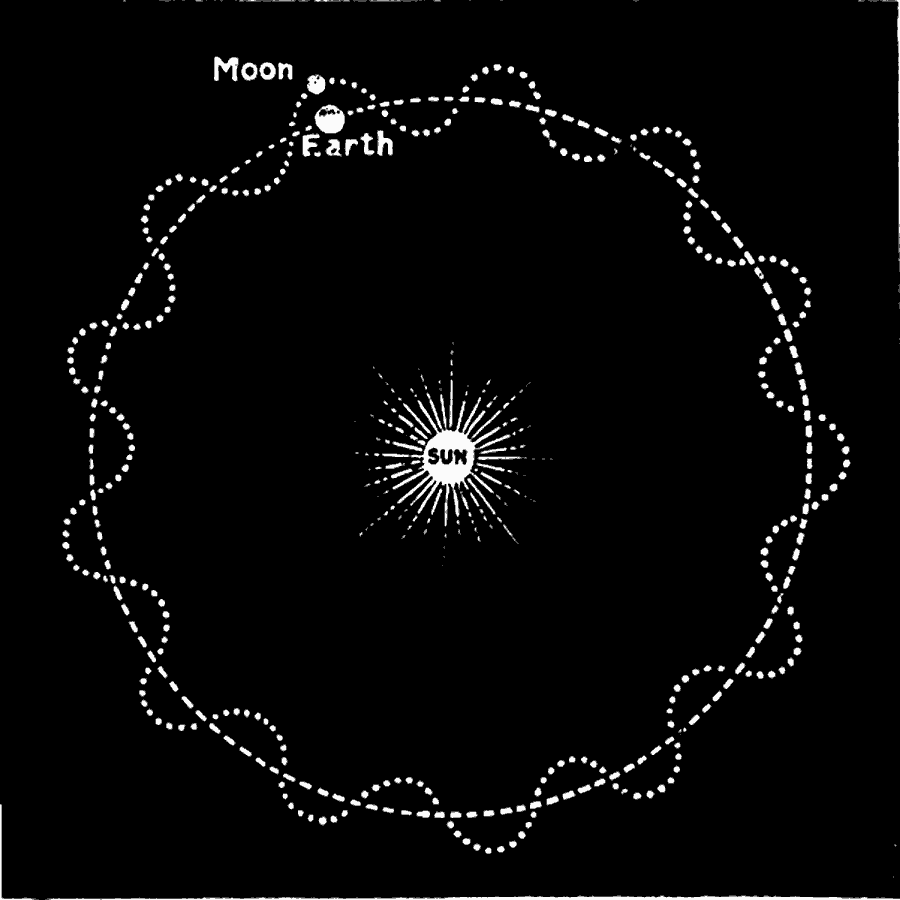
NRAO telescopes are open to all astronomers regardless of institutional or national affiliation. Operated under cooperative agreement by Associated Universities, Inc.įounded in 1956, the NRAO provides state-of-the-art radio telescope facilities for use by the international scientific community. The National Radio Astronomy Observatory is a facility of the National Science Foundation The app Earth Space Lab is designed especially for teaching the topic of the Earth as a planet at grammar or elementary schools (geography, physics). One year is 365 days, so every four years we add up the extra four quarters. If you want to see a nice historical account of how Johannes Kepler discovered the existence of elliptical orbits in the motion of the planets, see the How Stuff Works video on elliptical orbits. It takes the Earth 365-and-a-quarter days to go all the way around the Sun once. Elliptical orbits are much more general and allow for a wider range of initial conditions which existed when a planet/star system forms, thus making them a more probable solution for the properties of a planet’s orbital characteristics. This is due, for example, to the fact that when the Earth is closer to the Sun in its elliptical orbit it orbits faster, while when it is further away it orbits slower, averaging to a value equivalent to that of a circular orbit. Elliptical orbits are stable, possessing the same amount of total energy over the orbit as circular orbits. (Plese answer in the simplest form I’m only in middle school) - CheriĪnswer: In fact, a circular orbit is just a special case of an elliptical orbit. If all this isn't enough to make you feel you deserve an intergalactic speeding ticket, consider that we, along with our cousins in the Local Group, are hurtling at a truly astonishing 375 miles a second toward the Virgo Cluster, an enormous collection of galaxies some 45 million light-years away.Question: Why is the Earth’s revolution around the sun elliptical rather than a perfect circle? I feel like if there is the same amount of inertia and gravity acting on the Earth at all times, the revolution would end up being a circle, or at least closer to a circle than what it actually is. Our galaxy belongs to a cluster of nearby galaxies, the Local Group, and together we are easing toward the center of our cluster at a leisurely 25 miles a second. The Milky Way itself is moving through the vastness of intergalactic space. Even at this great speed, though, our planetary neighborhood still takes about 200 million years to make one complete orbit - a testament to the vast size of our home galaxy.ĭizzy yet? Well hold on. The Sun, Earth, and the entire solar system also are in motion, orbiting the center of the Milky Way at a blazing 140 miles a second. Perhaps that seems a bit sluggish - after all, Mars Pathfinder journeyed to Mars at nearly 75,000 miles per hour. Currently, the Earths orbital eccentricity is at about 0.0167, which means its orbit. In addition to this daily rotation, Earth orbits the Sun at an average speed of 67,000 mph, or 18.5 miles a second. Those fluctuations are likewise far milder in times of low eccentricity. The rate is higher at the equator and lower at the poles. For those of us living at Earth's midlatitudes - including the United States, Europe, and Japan - the rate is almost a thousand miles an hour. To begin with, Earth is rotating on its axis at the familiar rate of one revolution per day.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
